In this publication, we will consider the question of whether freon from the refrigerator is dangerous for human health. Let’s talk about three factors influencing refrigerants on people. We will separately tell about each of the freons for household refrigeration equipment. At the end of the article you will find answers to the most frequently asked questions. You can ask your question in the comments.
Refrigerants used in refrigerators
Modern refrigerators use several types of refrigerants. Manufacturers of refrigeration equipment fill new models with one of two types of freons:
- R134a, tetrafluoroethane;
- R600a, isobutane;
- R290 propane (very rare).
Older models were filled with more dangerous gases. They are not used now, but you can meet them. These are gases such as:
- R12, difluorodichloromethane;
- R22, difluorochloromethane.
Important
Often, craftsmen and service centers remake old refrigerators for modern refrigerants. This is due to the fact that obsolete freons are forbidden to use. Their value is constantly growing and finding them is becoming more difficult. Usually this procedure is performed during the repair. The most common substitutes are:
- Propane-butane mixtures;
- R406;
- R22 refrigerant analogues.
How to determine the type of freon
The type of refrigerant used can be found in the accompanying documentation (instructions, manual, specifications, etc.). It is also indicated on a sticker located in the main chamber of the refrigerator. If not, look for a sticker on the back of the refrigerator or compressor.
If the type of freon has been replaced, refrigerators indicate its type by sticking a special label on the compressor. The type of oil is also indicated there, if it was replaced.

Myths and truth about the dangers of freons
Modern refrigerants pose a low potential hazard to humans. It can harm health in three ways:
- Cause suffocation due to the replacement of air in the lungs;
- Have a toxic effect;
- Cause an explosion or fire.
Asphyxia
All freons used in refrigerators are heavier than air. When leaking, they accumulate at the bottom of the room. If you breathe in refrigerant, it will force the air out of your lungs. Asphyxia (suffocation) will begin. It can lead to loss of consciousness and death.
There is not enough freon in a household refrigerator to fill a kitchen or a room. Besides, it accumulates at the bottom. To inhale them, you have to try. In reality, this is only possible when refueling if there is a serious leak from the refrigerant bottle.
Poisoning
Refrigerator refrigerants have low or no toxicity. There are three options for getting poisoned:
- Inhale a large amount of freon at a time;
- Inhale the refrigerant in a small concentration for a long time;
- Swallow a certain amount of freon.
It’s hard to do all of this by accident. If the refrigerant leaks, it mixes with air and its concentration is low. Swallowing freon will not work, it has a low evaporation temperature. Unless you do it on purpose … To constantly inhale the refrigerant, you must always be in a room with a leaking refrigerator.
When burning or at high temperatures, the refrigerant may decompose into toxic components. It is difficult not to notice such a process, infrequently in the kitchen they use an open fire near the refrigerator. Achieving a high percentage of toxic substances in the air will be difficult.
Fire or explosion
R-290 and R-600a are highly flammable. In order for them to ignite, an open flame, spark or high temperature is needed. But modern refrigerators are designed in such a way that in the event of a leak, freon does not fall into risk areas – on wiring, electronic circuit boards.
The refrigerant may ignite under certain conditions. For example, the characteristics of isobutane R600a are such that it burns at a concentration of 1.4-8.5% in air. That’s a pretty narrow range to get into.
Interesting fact
Fires due to freon leakage in the refrigerator happen. But there are no statistics on them. Firefighters in such cases usually point to a faulty electrical wiring as the cause of the fire. This is partly true – if there was no short circuit, the refrigerant would not ignite.
Harm of different types of freons
All refrigerants used in refrigerators are heavier than air. When leaking, they accumulate in the lower part of the premises. Refrigeration equipment contains a small amount of refrigerant. Therefore, even a complete leak is not able to displace the air from the room.
Contact with freon on the skin, eyes, mucous membranes can lead to frostbite. In such cases, wash the damaged areas with warm water. In case of eye contact, do so within 15 minutes. If inhaled, move victim to fresh air.
In case of any exposure to freon with the human body, call emergency medical help. Some effects may not be noticeable immediately, but appear later. When working with refrigerants, use personal protective equipment:
- Glasses;
- Gloves;
- Respirator.
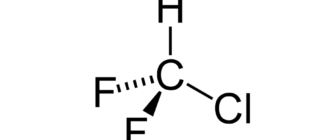
R12 (Difluorodichloromethane)
R-12 refrigerant was used in refrigerators produced before 1994. It has a good cooling capacity, but has a high ozone depletion potential. Prolonged inhalation of difluorodichloromethane can cause:
- Dizziness;
- Loss of concentration;
- arrhythmia;
- Depression of the central nervous system.
Freon R12 refers to slightly toxic non-flammable gases. When heated above 250 degrees Celsius, it decomposes with the release of:
- Of hydrochloric acid;
- hydrofluoric acid;
- Carbonyl halogenides.
hydrofluoric acid is also a powerful contact poison. Because of the ability of hydrofluoric acid to penetrate tissue, poisoning can occur readily through exposure of skin or eyes, or when inhaled or swallowed. Symptoms of exposure to hydrofluoric acid may not be immediately evident, and this can provide false reassurance to victims, causing them to delay medical treatment. Despite having an irritating odor, HF may reach dangerous levels without an obvious odor. HF interferes with nerve function, meaning that burns may not initially be painful. Accidental exposures can go unnoticed, delaying treatment and increasing the extent and seriousness of the injury. Symptoms of HF exposure include irritation of the eyes, skin, nose, and throat, eye and skin burns, rhinitis, bronchitis, pulmonary edema (fluid buildup in the lungs), and bone damage.
Source: Wikipedia article .
R134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane)
This refrigerant is considered the safest gas used in refrigerators. It is non-flammable, non-toxic, non-explosive. On contact with an open fire at a temperature of 250 ° C and surfaces heated to 370 ° C, it releases:
- Hydrogen fluoride;
- Carbonyl fluoride (carbonyl fluoride).
These substances are toxic. Their inhalation can lead to:
- Arrhythmias;
- Accumulation of fluid in the lungs.
R22 (Difluorochloromethane)
Freon R-22 has medium global warming and ozone depletion potentials. This gas is non-flammable, non-explosive, and has low toxicity. Prolonged exposure (inhalation) may cause:
- Dizziness and nausea;
- Loss of concentration;
- loss of consciousness;
- Drowsiness;
- General weakness;
- Arrhythmia and tachycardia.
When interacting with open flames and heated surfaces, the R22 refrigerant decomposes. This can produce toxic substances such as hydrogen fluoride. This requires a temperature above 220 degrees Celsius.
The formation of substances harmful to human health occurs at elevated pressure and oxygen concentration. Under normal conditions, toxic substances are released little, they can not harm health.
R290 (Propane)
Propane, or R290 refrigerant, is highly flammable. It lights up at a temperature of +470 °C. Therefore, it is practically not used in household refrigerators. With prolonged exposure, it negatively affects the nervous system. During combustion, the following may be released:
- Carbon monoxide;
- Carbon dioxide;
- Water.
R406a (Mix R-22, R-142b, R-600a)
Refrigerant R-406a is a three-component. It was developed to replace the banned R-12 freon. It consists of:
- R-22 (55%);
- R-142b (41%);
- R-600a (4%).
Freon R406a is not flammable and explosive. Due to toxicity, it can adversely affect human health. Short-term exposure (inhalation, ingestion) in high concentrations causes:
- Dizziness;
- Depression of the central nervous system;
- loss of consciousness;
- Impaired coordination.
With prolonged exposure in small doses, the following may develop:
- Decreased fertility;
- Violations of the development of the fetus in pregnant women;
- Cardiovascular diseases.
When heated, the components of the refrigerant begin to decompose. During the decomposition process, at temperatures above 250 degrees Celsius, the following are formed:
- Hydrofluoric acid;
- Carbonyl halides (especially toxic substances).
R600a (Isobutane)
R-600a refrigerant is often used in refrigerators, along with R-134a. It has zero ozone depletion potential and very low global warming potential. Isobutane is a non-toxic gas. Does not pose an immediate danger to humans.
Freon R600a is flammable. Illuminates on contact with an open flame or when heated to 460°C. During combustion and thermal decomposition, the following are released:
- Carbon monoxide;
- Carbon dioxide.
Summing up
Is freon from the refrigerator dangerous for human health? – Yes. But the likelihood of getting poisoned, harming health or causing a fire is minimal. Modern refrigerators use the safest refrigerants.
In the near future, the number of equipment on the most dangerous freons will be reduced. More efficient refrigerants are constantly being developed and introduced. Therefore, household refrigerators will be more reliable and safer to operate.
We hope the article was useful to you. You can leave your opinion in the comments. Don’t forget to share this post with your friends and colleagues !
Хотите получить помощь мастера, специалиста в этой сфере? Переходите на портал поиска мастеров Профи. Это полностью бесплатный сервис, на котором вы найдете профессионала, который решит вашу проблему. Вы не платите за размещение объявления, просмотры, выбор подрядчика.
Если вы сами мастер своего дела, то зарегистрируйтесь на Профи и получайте поток клиентов. Ваша прибыль в одном клике!